: Focused on temperature and humidity change

Rearch Goals
Temperature and Humidity:
A Close Relationship with Urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect
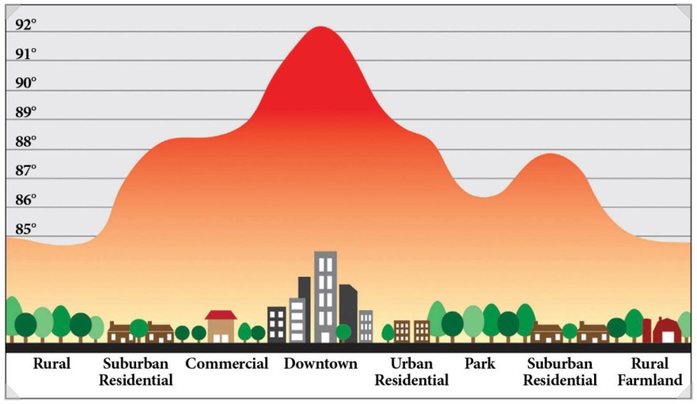
The urban heat island phenomenon (UHI) significantly impacts a city's climate, with the interaction of temperature and humidity playing a crucial role. High temperatures increase energy consumption and health risks, while humidity affects the intensity of UHI, especially during summer heat waves.
According to previous studies, meteorological factors such as precipitation were identified as variables that significantly influence the intensity of UHI (Lee and Baik, 2010; Kim et al., 2012). High humidity increases the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, thereby increasing the heat storage capacity, which can enhance the heat island effect (Paineburg, 2022). Wang et al. (2015) and Zhou et al. (2014) analyzed spatiotemporal SUHII according to urban shape and surface characteristics, highlighting the complex correlation between temperature and humidity for urban heat island phenomena. In addition, Debbage et al. (2012) and Peng (2011) studied seasonal and daily SUHII changes worldwide to identify the effects of these factors on urban heat island phenomena.
Therefore, based on these existing papers, this study aims to analyze the effect of changes in temperature and humidity on urban heat island phenomena and to find out the correlation between these two factors.